Fortran Allocate Array

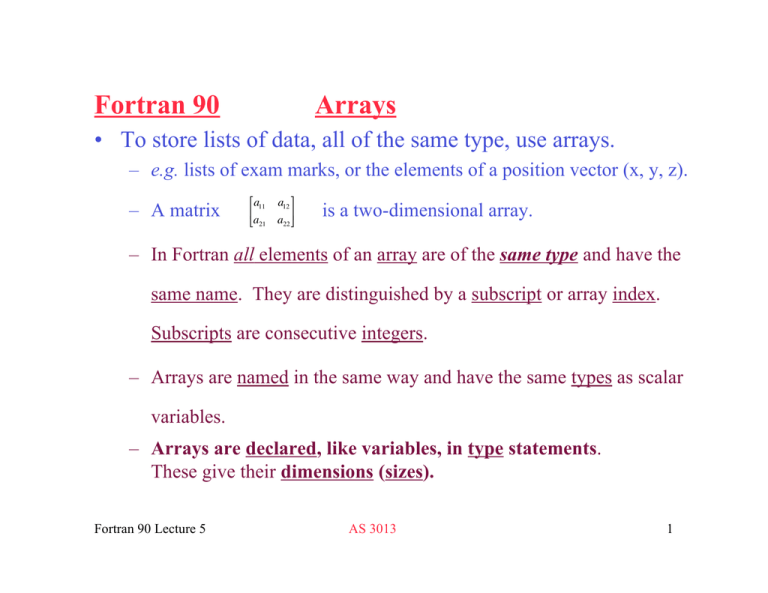
Fortran 90 Arrays

Fortran Allocatable Array Changes Pgi
3

7 1 11 Arrays
Returning Array From Function Issue 114 Fortran Lang Stdlib Github

Run Time Memory Allocation And Array Processing In Fortran Math 248 Docsity
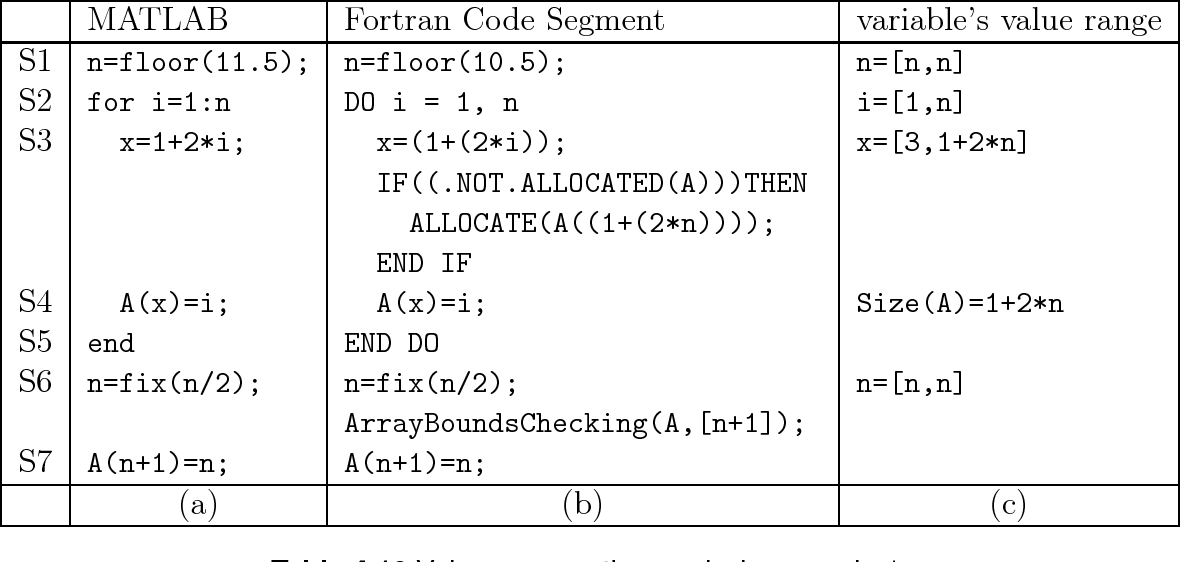
Fortran automatically lls the entire arrays with a single read statement, but does so by columns Once we transpose each array, you can see the ordering of the data in the array more closely matches the ordering in the le The last number read into array1 is the 00 to the right of the 14 on the second line of arraytxt.

Fortran allocate array. 216 DYNAMIC MEMORY ALLOCATION AND POINTERS (& Procedure Pointers) ***** (Thanks to Sergio Gelato who contributed some parts of this chapter;. Fortran Array Data and Arguments, Vectorization Examples The programmer can instruct the compiler to allocate aligned memory for arrays using compiler options (align array64byte) or directives (!dir$ attribute align) However, this is not sufficient for generating aligned vector code for loops The programmer should also tell the compiler. Allocate imax elements to two arrays, a and b Read in imax numbers to a and do the same to b Print out the arrays a, b and print out the sum of a and b Compare your attempt with sumallocf95 Array magic One of the benefits of arrays is that you can easily do operations on every element by using simple arithmetic operators.
Fortran 95 and later, with KIND argument Fortran 03 and later Class Inquiry function Syntax RESULT = SIZE(ARRAY, DIM , KIND) Arguments ARRAY Shall be an array of any type If ARRAY is a pointer it must be associated and allocatable arrays must be allocated DIM (Optional) shall be a scalar of type INTEGER and its value shall be. 3 Reading in array data A key feature of Fortran 90 that wasn’t available in Fortran 77 or earlier versions is the addition of ALLOCATABLE arrays With f77 you always needed to declare the size of the array at the onset of the program However, with the new syntax you can wait until later All you have to do is declare the shape. So check it has not been allocated first if (not allocated (foo)) then allocate (bar (10, 2)) end if Once a variable is no longer needed, it can be deallocated deallocate (foo) If for some reason an allocate statement fails, the program will stop.
3 Fortran thinks non allocated array is already allocated 2. When the Fortran 90 standard was being established, there was a request for this feature What we got was something a little different, in many respects more powerful, and in some respects intentionally crippled One underlying theme of new Fortran 90 constructs has been isolation of users from the details of memory allocation. Intel® Fortran Compiler Classic and Intel® Fortran Compiler (Beta) Developer Guide and Reference Developer Guide and Reference Version 214.
Furthermore, the size of the array (or matrix) returned by the function can be defined using values that are derived from the input parameters This feature is extremely useful when you write functions that return matrices or vectors, whose size depends on the size of. Although C has dynamic arrays (using new click here ) C cannot specify the size and shape of the array F90 provides much better support for dynamic arrays than C/C Defining, allocating and deallocating a ONEdimensional dynamic arrays. ALLOCATE ( A (N) ) where N is an integer variable that has been previously assigned To ensure that enough memory is available to allocate space for your array, make use of the STAT option of the ALLOCATE command ALLOCATE ( A (N), STAT = AllocateStatus) IF (AllocateStatus /= 0) STOP "*** Not enough memory ***".
Hi Guys, I'm a beginner in fortran programming and don't speak english so well, but i hope you will undersand my question ;) In the program there is an allocatable array, which shall be allocated in the subroutine, and then given back to the main program (beacause in the subroutine i read in the data and get to know how big the array must become). About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. Also, is there anything in F90 like Visual Basic's "ReDim Preserve" that allows you to allocate an array, fill it with something, and then reallocate to a larger size without losing your values?.
It has a fortran STOP in the end which frees the memory, when the code finishes However if I put a loop around it the code tries to allocate arrays which are already allocated One can check this issue quite conveniently whith the following command If (allocated(array(size))) deallocate (array) allocate(array). It is an error to allocate an array twice !. Fortran Programming Tutorials Dropbox link does not work!Website http//fluidiccoloursin/GitHub https//githubcom/arunprasaad2711/.
Answer (1 of 9) Yes, definitely However, the syntax is completely different and so are most of the semantics Here are the most important differences Fortran uses the code Allocate/code statement, not a code malloc()/code or code calloc()/code function Once. Array Slicing Syntax for Fortran For each dimension of an array, the full syntax of the print command to slice the array is print arrayexpression firstexpression lastexpression strideexpression where arrayexpression Expression that should evaluate to an array type. The DIMENSIONAttributeAttribute 1/61/6 zA Fortran 90 ppgrogram uses the DIMENSION attribute to declare arrays zThe DIMENSIONattribute requires three components in order to complete an array specification, rank, shape, and extent zThe rank of an array is the number of “indices” or “subscripts” The maximum rank is 7 (ie, sevendimensional).
The ALLOCATE statement creates space for allocatable arrays and variables with the POINTER attribute The DEALLOCATE statement frees space previously allocated for. 60 When allocating an array with the ALLOCATE statement, if SOURCE= or MOLD= is present and its expression is an array, the array can take its shape directly from the expression This is a lot more concise than using SIZE or UBOUND , especially for a multidimensional array. The only way to allocate aligned memory in standard Fortran is to allocate it with an external C function, like the fftw_alloc_real and fftw_alloc_complex functions Fortunately, Fortran 03 provides a simple way to associate such allocated memory with a standard Fortran array pointer that you can then use normally.
In Fortran 90, it is as simple as C = A B Most of the intrinsic functions operate componentwise on arrays C = sin (A) is equivalent to (in this case, A is a one dimensional array) do i=1,n C (i) = sin (A (i)) enddo Note C = A*B multplies corresponding. If the array is declared allocatable then the declaration only determines the rank of the array (the number of indices it will have), and memory is not actually allocated until the allocate statement is encountered By default, arrays in Fortran are indexed starting at 1 So if you declare. The rank of the array, ie, the dimensions has to be mentioned however, to allocate memory to such an array, you use the allocate function allocate ( darray(s1,s2) ) After the array is used, in the program, the memory created should be freed using the deallocate function deallocate (darray) Example.
Fortran 90 Free Form, ISO Standard, Array operations Fortran 95 Pure and Elemental Procedures Fortran 03 Object Oriented Programming Fortran 08 CoArrays Examples Installation or Setup Fortran is a language which can be compiled using compilers supplied by many vendors Different. Pgfortran stops at this point write(*,*) 'status = ', ierr write(*,*) 'well done!' end program test Execution of the program is terminated at the allocation. No matter if you are passing arrays in or out, always allocate them in C first, and you are (in C) responsible for the memory management Use Fortran to fill (or use) your arrays (that you own in C) If calling the Fortran exp_mesh subroutine from the c_exp_mesh subroutine is a problem (CPU efficiency), you can simply implement whatever the.
The ALLOCATED intrinsic function can be used to determine if an array is currently allocated Allocating storage for structures By using the ALLOCATE statement, it is also possible to allocate memory for a structure referenced only by a pointer The following example, though trivial, illustrates the idea REAL,POINTERx ALLOCATE(x) x=10. Thanks to Keith Bierman and Eric Grosse for the help with the procedure pointers section) In standard FORTRAN 77, the sizes of all objects must be known at compile time (This does not apply to the sizes of formal arguments to. Arrays When you allocate an array in F90, are the values guaranteed to be set to zero or must you still explicitly initialize?.
Array allocation in Fortran subroutine 2 Passing an allocated array from a SUBTROUTINE to the main program in Fortran 1 Why does Fortran spend so much time on 'for_allocate' or 'for_deallocate'?. Each character occupies 8 bits of storage, aligned on a character boundary Character arrays and common blocks containing character variables are packed in an array of character variables The first character of one element follows the last character of the preceding element, without holes The length, len must be greater than 0. Thanks in advance Julie.
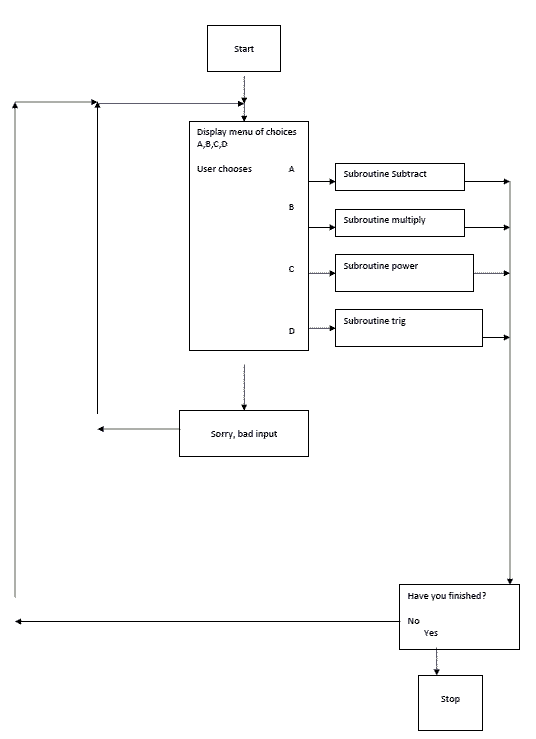
Allocatable Arrays In the old days, the maximum size arrays had to be declared when the code was written This was a great disadvantage, as it resulted in wasted RAM (arrays size had to be the maximum possible) or in frequent recompilations Fortran90 allows for "allocatable" arrays you to use onlyallocatable arrays in your codes. Using Array Space in Subprograms As I mentioned before, Fortran simply passes the address of a variable to a subroutine This makes it easy to allocate space for an array at one level in your program, and then use that space in subroutines called or functions used by that level. (c) Two integer arrays one of rank 2 the other of rank 3 (d) A rank one real array with lower and upper bound of n and n respectively Write allocation statements for the arrays declared in question 1, so that (a) The array in 1 (a) has 00 elements (b) The array in 1.
Arrayvalued functions functions that return arrays Functions in Fortran 90 can even return arrays (or matrices) !. A program below is an example of reallocation for array already allocated program test integer, allocatable, dimension() foo integer ierr allocate(foo(100), STAT=ierr) write(*,*) 'status = ', ierr allocate(foo(100), STAT=ierr) !. Fortran 90 Lecture 5 AS 3013 Arrays Memory allocation •Memory for arrays that are not local to a subprogram is allocated by the calling program, ultimately by the main program •But you may not know the actual size of your datasets, or they may vary.
532 Views When an allocatable array is to be passed as an argument to a subroutine, an explicit interface to the subroutine must be available to the compiler For example fortranProgram test real, allocatable array (,) call mysub (array) contains subroutine mysub (a) real, allocatable a (,) allocate (a (10,10)) end subroutine. Uses dynamic allocation multidim array initialization cannot put dimensions inside the brackets, it must be done this way. ALLOCATE(ARRAY(1ASZ)) ARRAY => REALLOCATE(ARRAY,ASZ100) I'll say instead that arrays are much more fundamental to Fortran than to C (and even more so to f90 than they were to f77) If REALLOCATE is defined in Fortran, it will certainly need to apply to.
Fortran arrays are very powerful and allows to define matrices vectors other arrays with up to 7 dimensions Arrays Syntax & arrays sections Arrays syntax In older Fortran codes, arrays are usually accessed element by element while in modern. Homework Statement I have character array in fortran which is defined as allocatable When program runs, user inputs something like 1,2,3,4, and then program reads it and counts the particles, and then allocate array with dimension it just read Thats' how I understood it This program. ALLOCATED(ARRAY) and ALLOCATED(SCALAR) check the allocation status of ARRAY and SCALAR, respectively Standard Fortran 90 and later Note, the SCALAR= keyword and allocatable scalar entities are available in Fortran 03 and later Class Inquiry function Syntax.
Declare and initialize a 3D array x, having dimensions boundaries m, n, p, and containing real numbers X array (1 M, 1 N, 1 P) of Float = (others => (others => (others => 10)));. Lahey/Fujitsu Fortran ALLOCATE Statement If the object of an ALLOCATE statement is an array, the ALLOCATE statement defines the shape of the array Syntax ALLOCATE (allocationlist , STAT=statvariable) Where allocationlist is a commaseparated list of pointer or allocatable variables Each allocatable or pointer array in the.

Fortran Array Allocation Overflow Stack Overflow

無料ダウンロード Fortran Allocate
Faculty Washington Edu

Fortran 90 Performance Problems Acm Sigplan Fortran Forum

Allocate Multiple Arrays With Single Shape Stack Overflow
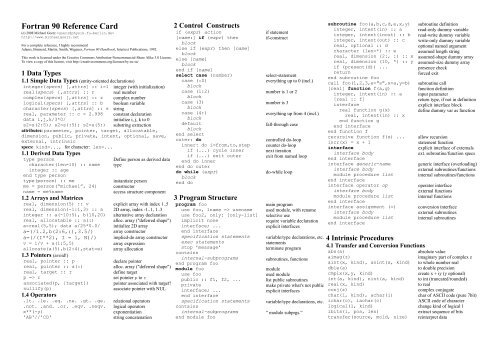
Fortran 90 Reference Card
Fortran Programming Tutorials Revised 015 Characters Strings String Arrays Youtube

Arrays 2 Further Examples Springerlink
Carson Math Uwm Edu
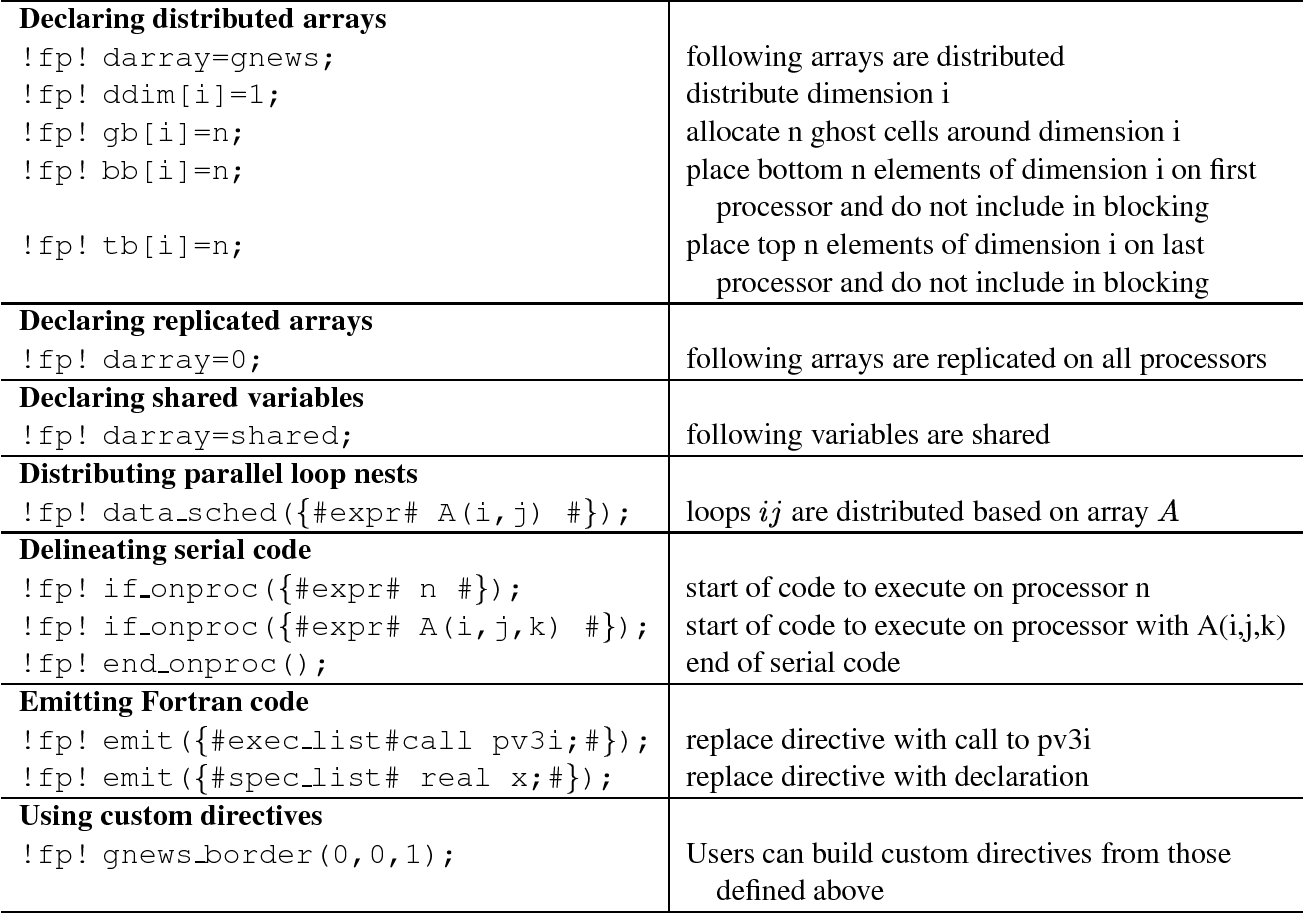
A Programmable Preprocessor For Parallelizing Fortran 90 Semantic Scholar

Why Does A Subroutine With An Array From A Use Module Statement Give Faster Performance Than The Same Subroutine A Locally Sized Array Stack Overflow
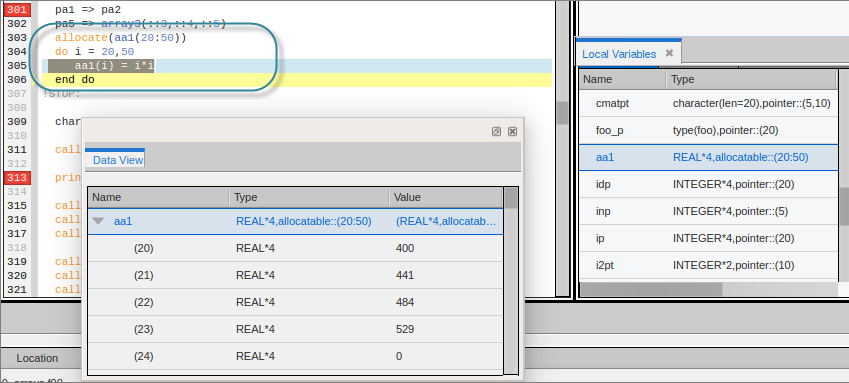
Fortran 90 Deferred Shape Array Types
Pdf Mcfor A Matlab To Fortran 95 Compiler Semantic Scholar
Multi Dimensional Arrays Ppt Video Online Download

Pdf Generic Programming In Fortran 90 Arjen Markus Academia Edu

Intel Fortran Libraries Reference Maxloc Array Mask Manualzz
Forums Silverfrost Com View Topic Pack Function

Interoperability With C In Fortran 03 Megan Damon

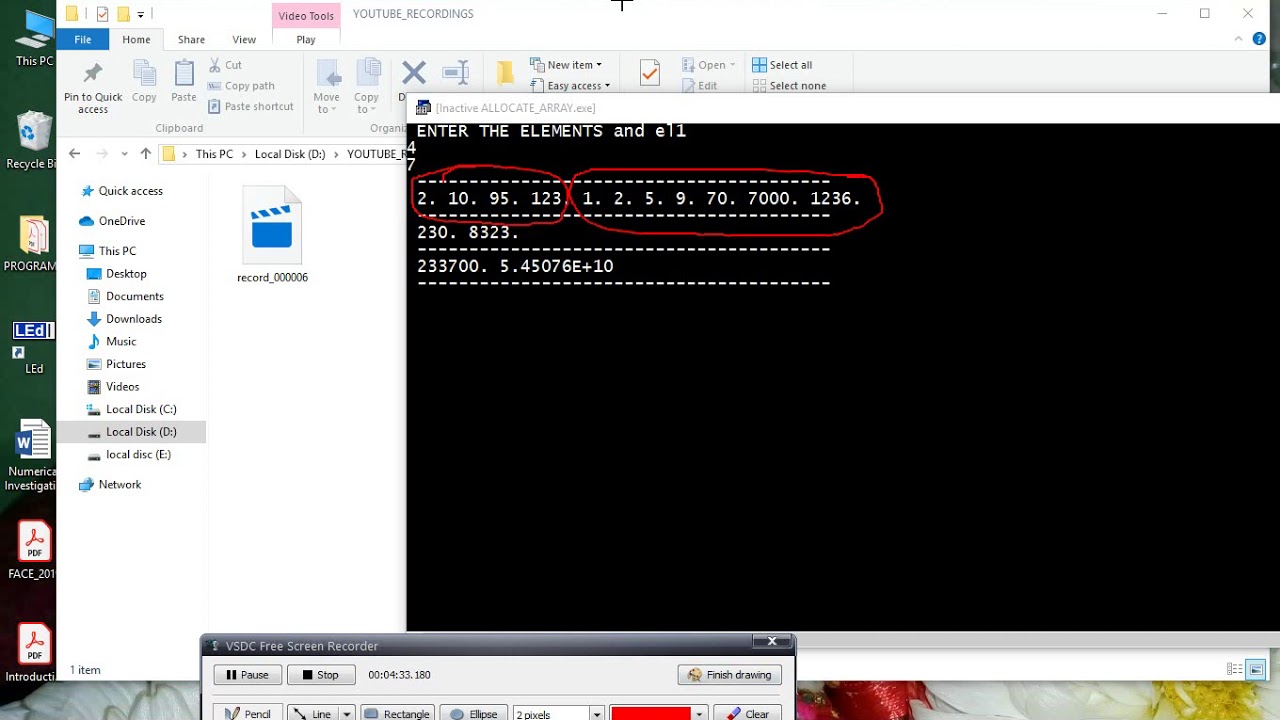
Fortran Get The Median In A Dynamically Allocated Array Youtube
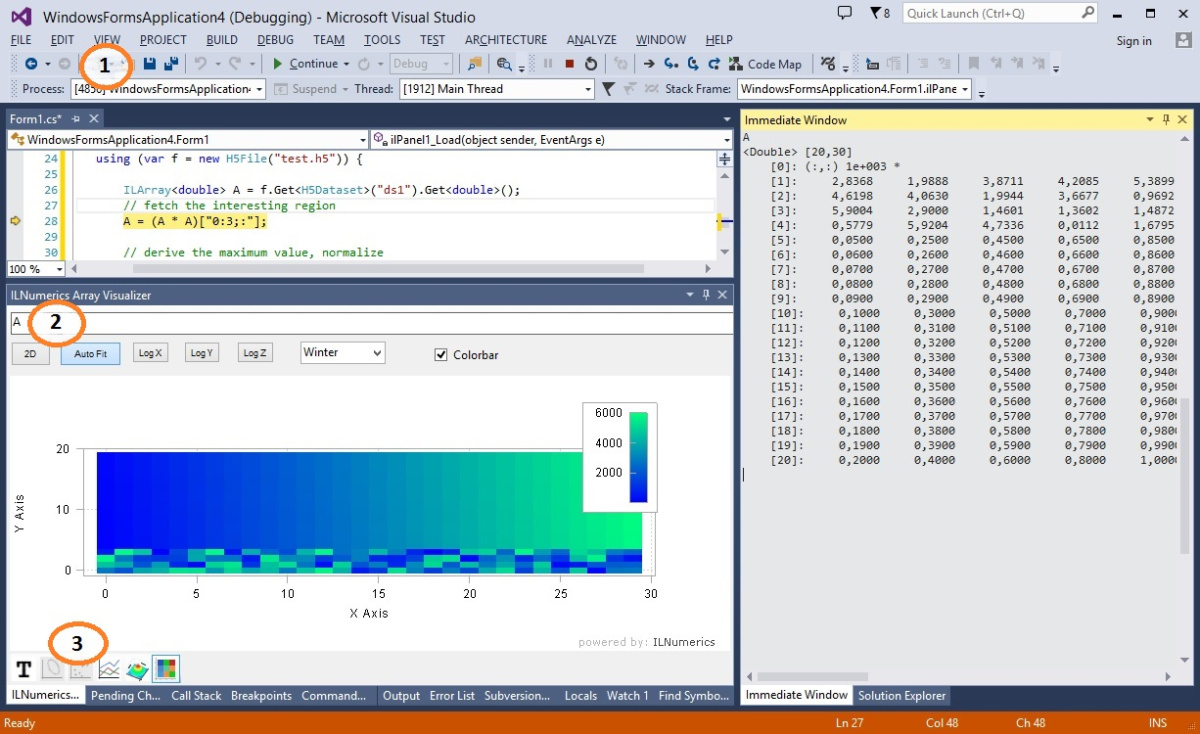
Ilnumerics High Performance Computing Tools

Fortran Array Features Session Five Icocsis Outline 1 Zero Sized Array 2 Assumed Shaped Array 3 Automatic Objects 4 Allocation Of Data 5 Elemental Operations Ppt Download
Object Oriented Programming Via Fortran 90 Emerald Insight

Example Illustrating The Handling Of Common Variants By Emulating The Download Scientific Diagram

Fortran 90 Arrays

Introduction To Fortran Serial Programming A Simple Example

Solved The Programming Language Is Fortran 90 Please Use Chegg Com
1
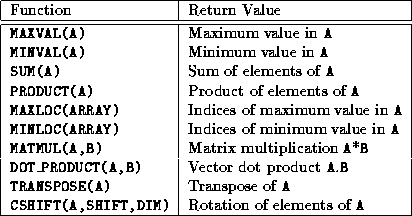
7 2 Fortran 90

Pdf Avoiding Memory Leaks With Derived Types

Application Of Fortran 90 To Ocean Model Codes
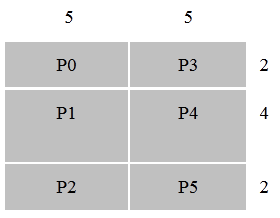
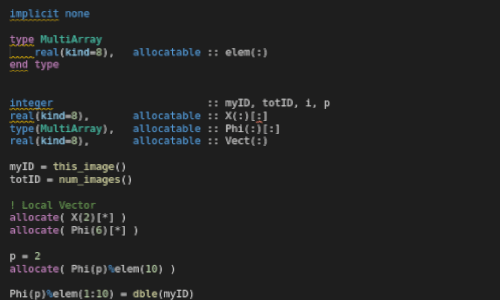
Pnnl Global Arrays Toolkit Fortran Api
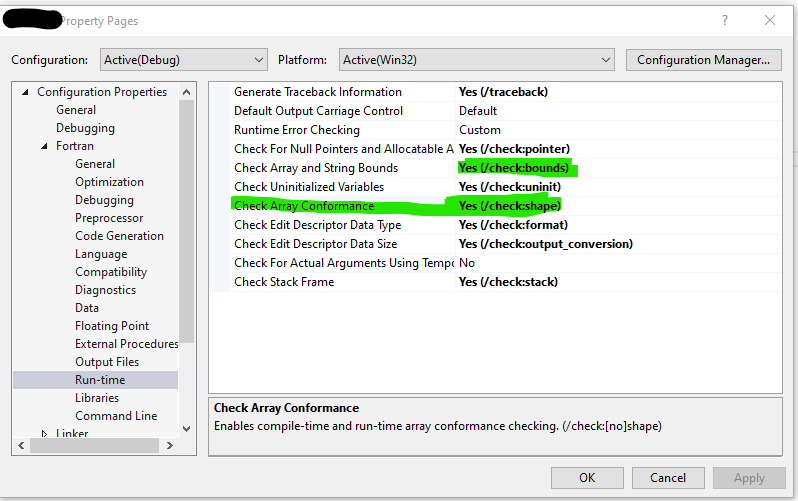
Problems With Allocatable Arrays Real8 Accessing Ranges Not Allocated In Arrays In Fortran Intel Communities
Hpc Forge Cineca It

Solved Debug Issue Relating To Allocatable Variables In User Defined Type Constructs Status Intel Communities
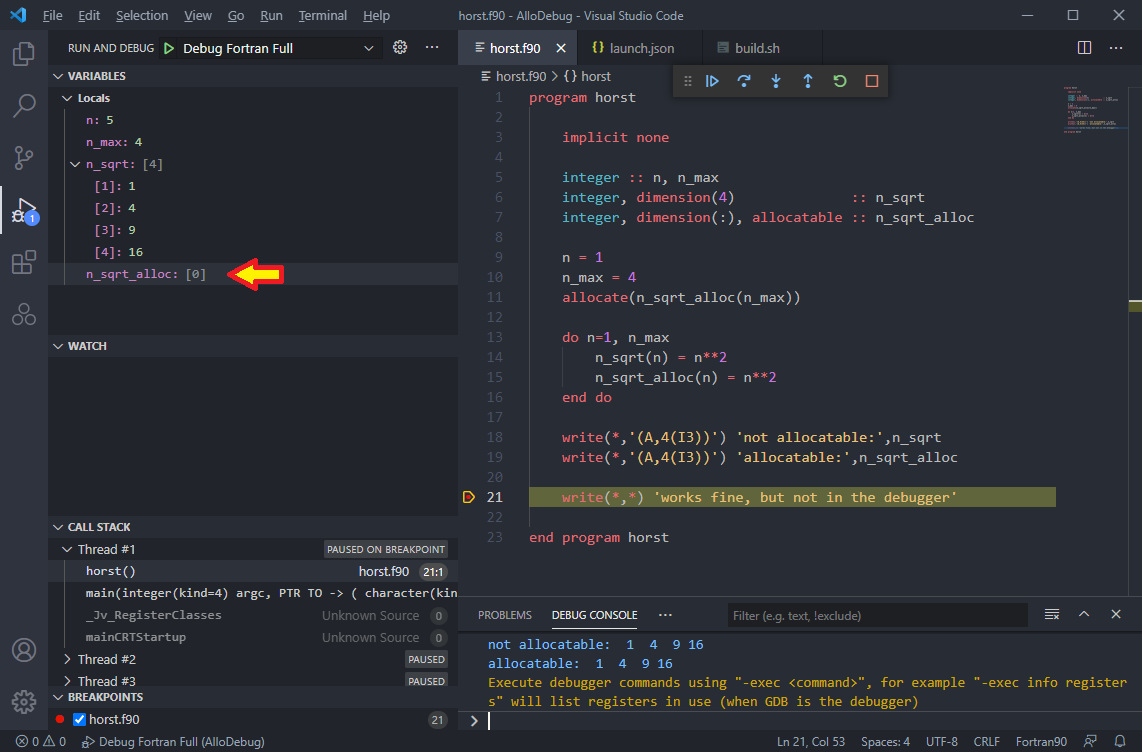
Gdb Debugger Allocatable Arrays Not Shown Githubmemory

無料ダウンロード Fortran Allocate
Fortran Programming Tutorials Revised 024 Formats Arrays Allocate Limits Of Int Youtube

Introduction To Fortran 90 Pointer Variables Qub

Fortran 90 Yetmen Wang Fortran 90 95 00 Introduction Fortran Versions Program Structure New Source Form Oo Programming Array Programming Significant Ppt Download

Analyzing Stock Price Time Series With Fortran Arrays Part 3 Manning

Fortran An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Solved Scc374c 394c Parallel Computing For Science And Chegg Com

Fortran 90 Tutorial Grdelin

Fortran Programming Tutorials Revised 037 Fortran Array Indexing Printing Arrays Youtube

Introduction To Fortran Serial Programming A Simple Example

Uni Texus Austin

Access Violation When Writing To A Fortran Allocatable Array Stack Overflow

Dynamically Allocated 2d Array C Slide Share
5 Analyzing Time Series Data With Arrays Modern Fortran Building Efficient Parallel Applications

Application Of Fortran 90 To Ocean Model Codes

Does Fortran Make Copies Of Array Sections Passed To Function Subroutine Stack Overflow

7 2 Fortran 90

Array Dimension An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Fortran 90 Gotchas Part 3 Acm Sigplan Fortran Forum
Fortran For Scientific Computing

How To Program In Fortran With Pictures Wikihow
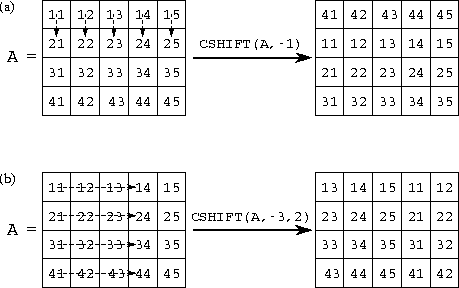
7 2 Fortran 90

Julia Vs Fortran Syntax Fortran Discourse

C Dynamic 2d Array Code Example

Arrays The Need For Arrays Z Up Until
1

Pass A Fortran Derived Type Which Contains Allocatable Array Between Different Compilers Pgi And Intel Stack Overflow
Faculty Washington Edu

Application Of Fortran 90 To Ocean Model Codes Mark Hadfield National Institute Of Water And Atmospheric Research New Zealand Ppt Download
Fortran 90 Arrays
Fortran Tutorial Free Guide To Programming Fortran 90 95 Advanced Topics
How To Allocate An Array In Fortran Youtube

無料ダウンロード Fortran Allocate

How To Optimize Data Transfers In Cuda Fortran Nvidia Developer Blog

Fortran Wikipedia

無料ダウンロード Fortran Allocate

Essence Of Fortran Multi Dimensional Array Emulation In C We Note Download Scientific Diagram
5 Reasons Why Fortran Is Still Used
Modern Fortran By Example 5 Arrays And Plotting Part 1 Youtube

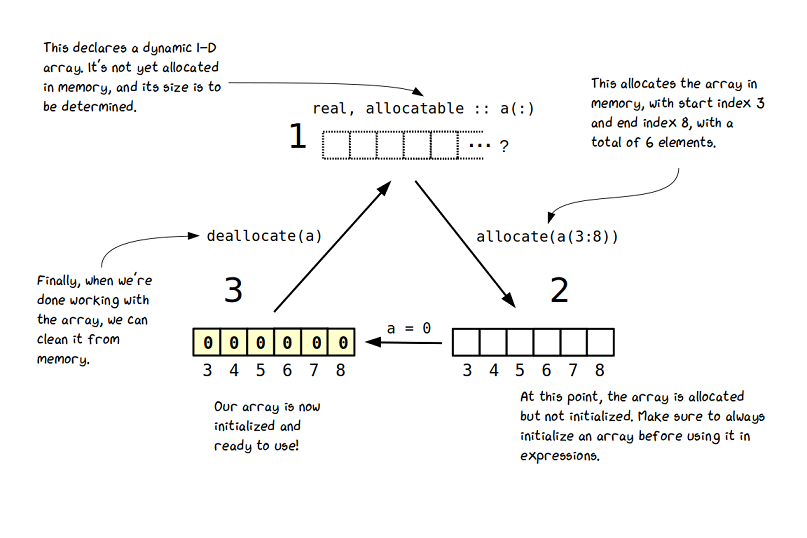
Fortran Dynamic Arrays

無料ダウンロード Fortran Allocate

Write Function In Fortran Stack Overflow
1

How To Prevent Using Heap Arrays Without Stack Overflow Fortran Discourse

Essence Of Fortran Multi Dimensional Array Emulation In C We Note Download Scientific Diagram

Fortran Array Features Session Five Icocsis Outline 1 Zero Sized Array 2 Assumed Shaped Array 3 Automatic Objects 4 Allocation Of Data 5 Elemental Operations Ppt Download
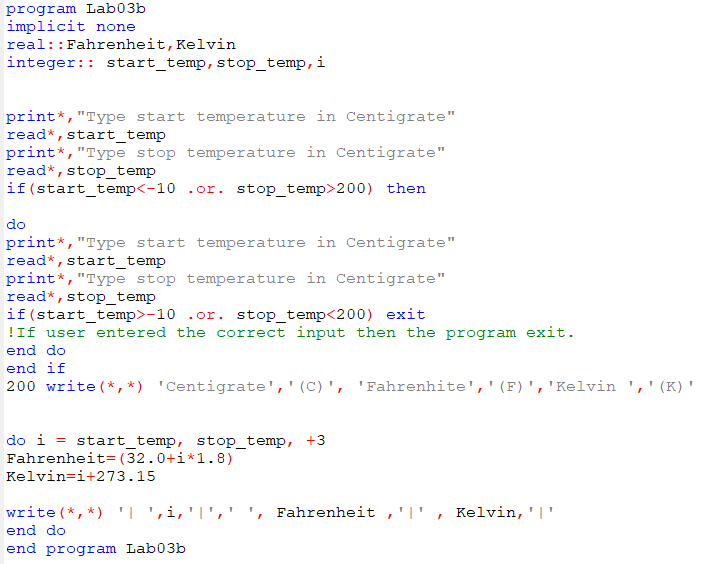
Lab04 Use Of Dynamic Array Modify The Part B Of Lab03 Chegg Com
Tutorialspoint Com

Fortran 90 Arrays

Application Of Fortran 90 To Ocean Model Codes
Web Gps Caltech Edu

Fortran 90 Basics
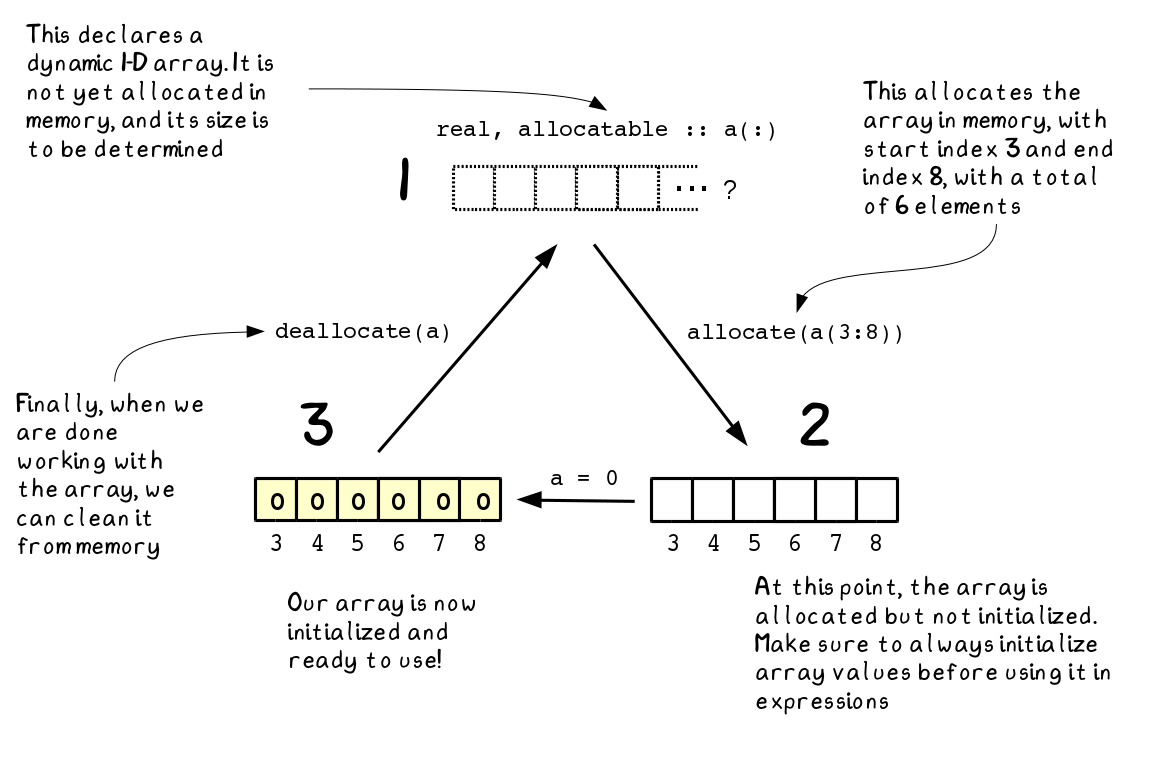
Analyzing Stock Price Time Series With Modern Fortran Part 2 By Milan Curcic Modern Fortran Medium

Program Fortran 90 Implementing The Quick Sort Algorithm Download Scientific Diagram
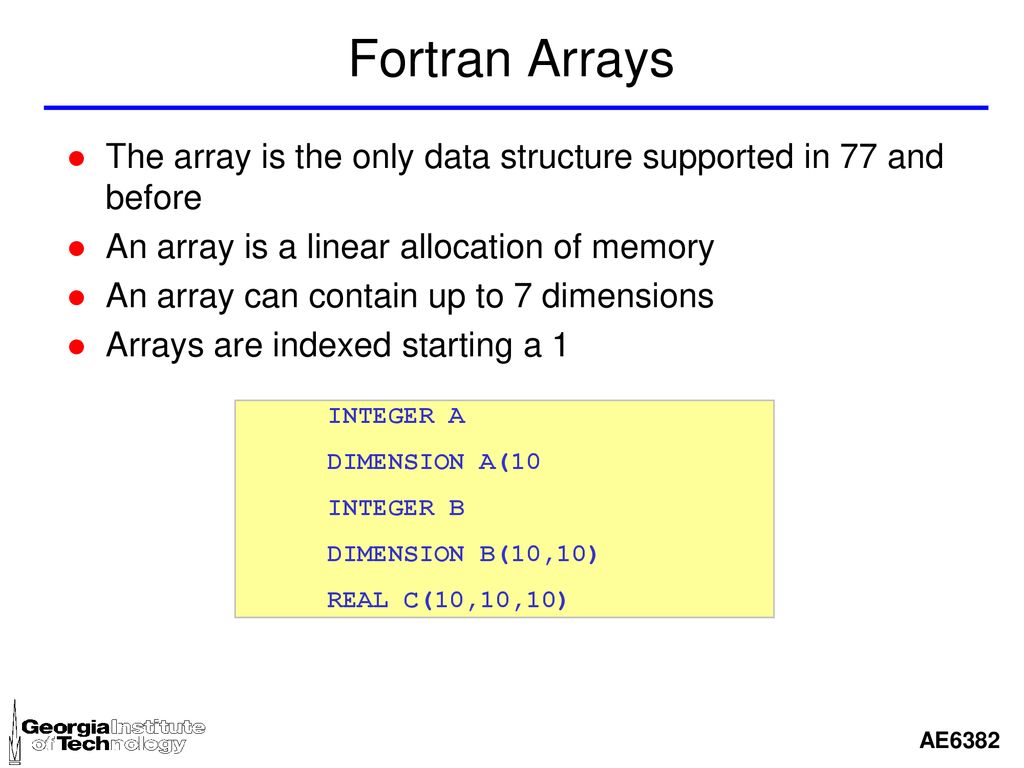
History Of Computing Fortran Ppt Download
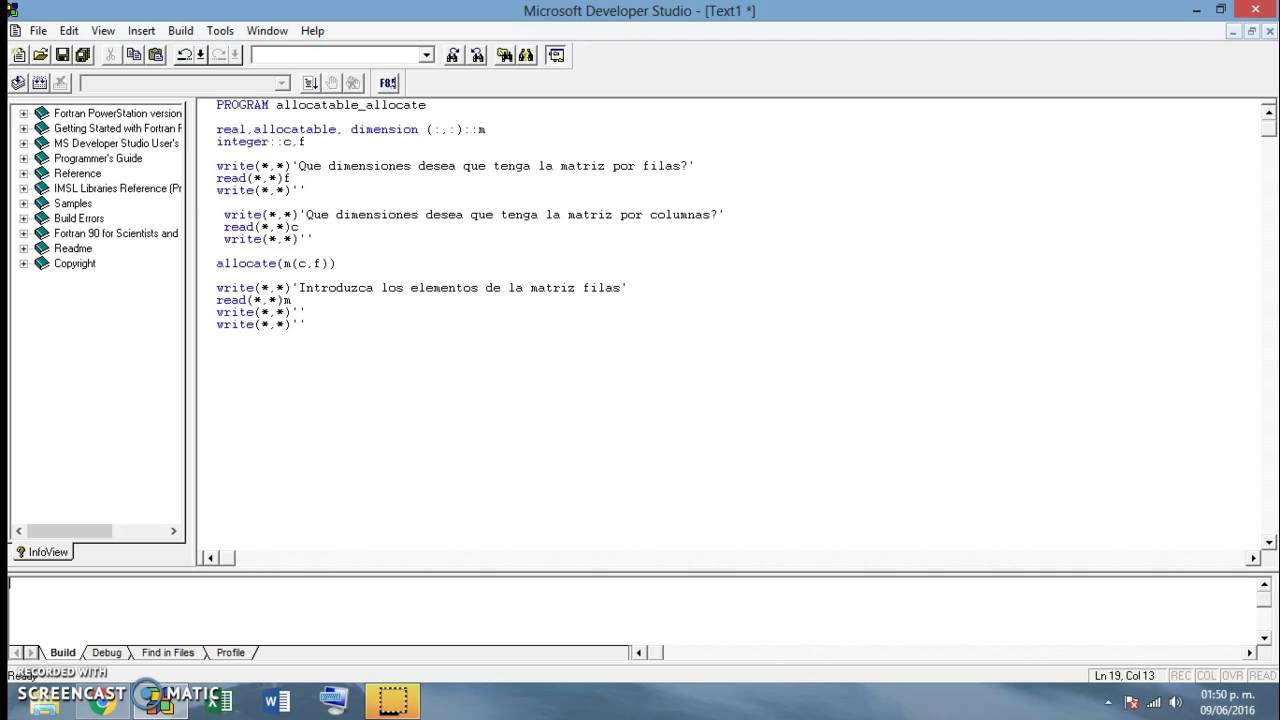
Comando Allocatable Para Fortran Youtube

Data Structuring In Fortran Springerlink

Fortran Debugging In Osx With Visual Studio Code Random Bits
Cds Cern Ch

Problems With Allocatable Arrays Real8 Accessing Ranges Not Allocated In Arrays In Fortran Intel Communities

Ppt Data Types Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

Fortran Sigsegv After Successfully Creating Array Of Pointers Stack Overflow

Fortran 90 95 And Fortran 90 Generalities Format Changes Portable Numerics Arrays Syntax Classes Of Arrays Dynamic Storage Structures Ppt Download



